Table of Contents
- – Comprehending the Eating Disorder-OCD Link
- – Eating Disorders in Athletes and Dancers: A Sp...
- – OCD Treatment: Beyond Contamination Anxieties
- – EMDR Intensives for Trauma-Based Eating Disorders
- – Sehrish Ali
- – Anxiety Therapy as Foundation for Recuperation
- – Searching For Specialized Therapy for Lasting ...

The crossway of consuming problems and obsessive-compulsive problem stands for among one of the most difficult presentations in mental health therapy. These conditions often share underlying patterns of stiff reasoning, anxiety-driven behaviors, and tries to regulate unpredictability via ritualistic activities. For athletes, professional dancers, and individuals with perfectionist propensities, these disorders can come to be particularly entrenched, woven into identification and efficiency in methods that make acknowledgment and therapy extra intricate.
Comprehending the Eating Disorder-OCD Link
Eating conditions and OCD share considerable neurobiological and emotional overlap. Both problems include invasive thoughts, uncontrollable actions, and heightened anxiety when routines are interrupted. Research indicates that about 40% of individuals with eating problems also fulfill criteria for OCD, suggesting these conditions might represent different expressions of similar underlying susceptabilities.
The connection between these disorders often manifests as a vicious circle. Compulsive ideas regarding food, body shape, or weight drive compulsive consuming habits, workout rituals, or restrictive patterns. These behaviors temporarily reduce anxiety, reinforcing the cycle and making it considerably harder to break. Over time, what started as attempts to take care of anxiousness or accomplish details goals advances into an inflexible system that controls every day life.
Consuming condition treatment that deals with these obsessive-compulsive functions needs specialized understanding. Generic strategies to disordered eating might miss the anxiety-driven devices preserving behaviors, while standard OCD treatment could ignore the body picture and identity elements central to eating problems. Integrated therapy comes close to identify this intricacy and address both the obsessive-compulsive patterns and the certain attributes of disordered consuming.
Experts specializing in this intersection, such as those at Live Mindfully Psychiatric therapy, recognize that reliable therapy needs to address multiple layers all at once. This includes collaborating with the cognitive rigidity attribute of both problems, the underlying stress and anxiety driving habits, and the identity elements that make modification really feel threatening.
Eating Disorders in Athletes and Dancers: A Special Challenge
Professional athletes and professional dancers face specific susceptability to eating disorders, with occurrence prices dramatically more than in the general population. The emphasis on body composition, weight demands, and aesthetic ideals in these areas develops an environment where disordered consuming can develop under the guise of dedication or expertise. What begins as "" clean eating"" or "" optimum fueling"" can slowly evolve into restrictive consuming conditions that compromise both health and wellness and efficiency.
The sports and dance neighborhoods typically stabilize behaviors that would certainly be identified as disordered in other contexts. Prolonged training sessions, stiff meal timing, compulsive body checking, and exercise obsession might be deemed indications of dedication instead of alerting indications. This normalization makes it harder for professional athletes and dancers to acknowledge when their connection with food and exercise has crossed into pathological territory.
Perfectionism, extremely valued in sports and artistic pursuits, acts as both a threat element and preserving system for consuming conditions. The exact same high qualities that drive excellence-- self-control, focus to detail, high standards-- can fuel compulsive patterns around food and body. Professional athletes and dancers typically fear that resolving their eating problem will jeopardize their performance, not acknowledging that the problem itself is limiting their potential via physiological exhaustion and emotional preoccupation.
Specialized consuming disorder treatment for athletes and professional dancers need to browse these unique dynamics. Therapy approaches that honor the individual's dedication to their sporting activity or art while attending to the dangerous patterns prove most efficient. Therapists dealing with these populations understand sport-specific stress and can assist customers establish much healthier relationships with food and body without needing them to desert their athletic or creative quests.
OCD Treatment: Beyond Contamination Anxieties
While several associate OCD with contamination concerns and hand washing, the condition manifests in varied methods. Intrusive ideas about injury, sexual web content, religious problems, or proportion can be equally stressful. For individuals with eating conditions, OCD typically includes fixations about food, contamination concerns concerning eating, or compulsions around workout and body checking.

Efficient OCD therapy typically entails exposure and action avoidance (ERP), a therapy approach that assists people face feared situations while resisting compulsive responses. For consuming disorder discussions with OCD features, this could consist of exposures to been afraid foods, lowering body checking behaviors, or tolerating unpredictability around consuming choices. The process is progressive and personalized, valuing each individual's preparedness while challenging evasion patterns that maintain stress and anxiety.
Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderCognitive-behavioral therapy for OCD aids individuals acknowledge the idea patterns that fuel compulsions. Learning to identify compulsive thoughts without engaging with them through rituals confirms central to recovery. This metacognitive recognition-- the ability to observe thoughts without instantly believing or acting on them-- stands for a critical ability that profits both OCD and eating condition recovery.
Several individuals with OCD and eating disorders also deal with perfectionism, seeing anything much less than complete control as failure. This all-or-nothing reasoning reaches therapy itself, with individuals in some cases believing they have to be "" best"" at recuperation. Therapy must address these perfectionistic requirements, helping customers establish self-compassion and resistance for the unpleasant, nonlinear nature of healing.
EMDR Intensives for Trauma-Based Eating Disorders
Progressively, medical professionals acknowledge that several eating conditions have origins in traumatic experiences. Whether developing trauma, details stressful events, or the accumulation of unfavorable experiences, unsettled injury commonly underlies the demand for control that consuming disorders give. EMDR intensives use a concentrated technique to refining these distressing foundations, addressing the much deeper chauffeurs of disordered eating.
EMDR intensives press treatment into prolonged sessions over days rather than weeks, permitting for more detailed handling. For eating problem therapy, this intensive layout can accelerate progress by addressing multiple stressful memories or experiences in a concentrated timeframe. The strategy verifies particularly valuable for individuals who have completed typical eating condition therapy but proceed dealing with underlying anxiousness or trauma-related triggers.
Sehrish Ali
The link between trauma and eating conditions shows up in numerous means. For some, disordered consuming stands for an effort to reclaim control after experiences of powerlessness. For others, body frustration connects to messages gotten during developmental years or particular traumatic experiences. EMDR helps reprocess these memories and linked beliefs, decreasing their emotional fee and enabling for more flexible self-perception.
Incorporating EMDR intensives with ongoing eating problem therapy and nutritional assistance develops a detailed treatment strategy. While EMDR addresses underlying injury, simultaneous assistance helps people create new coping systems and keep recovery-oriented actions. This incorporated method recognizes that eating problems offer features in individuals's lives, and lasting modification requires both processing what drove the problem and building different methods of taking care of distress.
Anxiety Therapy as Foundation for Recuperation
Stress and anxiety underlies both consuming disorders and OCD, making stress and anxiety management abilities important for recovery. Learning to tolerate uncertainty, handle physical stress and anxiety sensations, and respond to hard feelings without resorting to disorder behaviors represents core operate in treatment. Anxiety therapy provides these foundational skills while aiding individuals understand their unique stress and anxiety patterns.
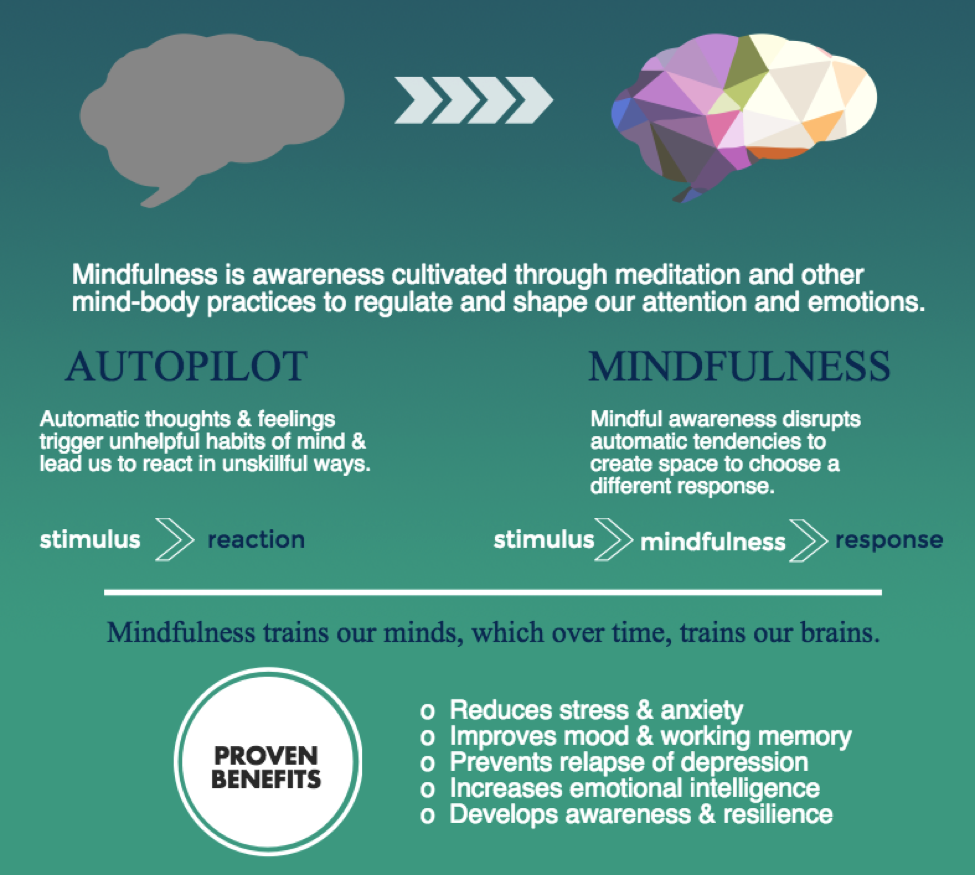
Mindfulness-based strategies confirm particularly useful for consuming problem and OCD treatment. These methods help individuals observe thoughts and experiences without instantly responding, developing room between triggers and responses. For someone with an eating condition, mindfulness could involve seeing anxiety around food selections without automatically limiting. For OCD presentations, it might suggest observing invasive ideas without engaging in uncontrollable reactions.
Somatic strategies to stress and anxiety treatment address the body-based elements frequently neglected in cognitive therapies. Numerous people with eating problems and OCD experience increased interoceptive awareness-- sensitivity to interior physical sensations-- which can drive stress and anxiety and uncontrollable actions. Learning to manage the nerve system via breath job, modern leisure, or other somatic strategies provides concrete devices for managing stress and anxiety in real-time.
Searching For Specialized Therapy for Lasting Recovery
Recuperation from consuming conditions and OCD needs specialized therapy that attends to the one-of-a-kind functions of these conditions. Generic methods may offer short-term relief but usually miss out on the maintaining systems that drive regression. Therapists with particular training in consuming conditions, OCD, and injury comprehend these nuances and can offer targeted interventions that resolve origin instead of simply symptoms.
When seeking therapy, take into consideration therapists that incorporate multiple evidence-based techniques instead than relying upon a solitary method. Eating problems and OCD seldom respond to one-size-fits-all therapy, and adaptability in strategy enables therapists to adjust treatments to individual demands. In addition, cooperation with other service providers-- such as dietitians, doctors, and psychiatrists-- frequently confirms crucial for detailed treatment dealing with all elements of recuperation.
Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderFor professional athletes, professional dancers, and nit-pickers dealing with consuming conditions or OCD, discovering a specialist that comprehends these certain contexts makes substantial difference. Therapy that honors your values and goals while attending to harmful patterns produces the structure for lasting recovery that improves instead of limitations your life and quests.
Table of Contents
- – Comprehending the Eating Disorder-OCD Link
- – Eating Disorders in Athletes and Dancers: A Sp...
- – OCD Treatment: Beyond Contamination Anxieties
- – EMDR Intensives for Trauma-Based Eating Disorders
- – Sehrish Ali
- – Anxiety Therapy as Foundation for Recuperation
- – Searching For Specialized Therapy for Lasting ...
Latest Posts
Why Brainspotting Facilitates Healing in Processing Trauma
How Traditional Eating Disorder Treatment Needs Enhancement Unless It Includes Trauma Processing
Locating the Right Mental Wellness Assistance: An Extensive Take A Look At Stress And Anxiety, Anxiety, and Trauma Therapy Choices
Navigation
Latest Posts
Why Brainspotting Facilitates Healing in Processing Trauma
How Traditional Eating Disorder Treatment Needs Enhancement Unless It Includes Trauma Processing